
Hiroshi Asanuma
Chiba University, Japan
Title: Novel Applications of Smart Materials and Structures Aiming at Disaster Mitigation
Biography
Biography: Hiroshi Asanuma
Abstract
The author et al. have proposed to use novel materials/technologies such as smart materials/structures and related technologies to enable revolutionary prevention/mitigation of disasters. The deployable breakwater shown in Figure 1 is an example, which can be used daily for energy harvesting, small enough not to become an obstacle, and a smart breakwater deployable by force and material of tsunami etc.1) The author et al. discussed new approaches which enable sustainability as well as disaster mitigation, and named it “Disaster Mitigation and Sustainable Engineering.” Then the author developed a committee in JSME M&P division. In this presentation, smart disaster mitigation strategies especially based on smart materials/structures are described. To realize the concept, two elemental researches, i.e. artificial forest and novel deployable structure based on honeycomb are examined.1) The researches below are also undergoing by the author and/or his collaborators. (i) Applications of piezoelectric polymers in electrical power generation using ocean waves (Su). (ii) Dynamic deployment of smart inflatable tsunami airbags (Shahinpoor).2) (iii) A novel underwater inflatable structures for smart costal disaster mitigation (Adachi). (iv) SHM of pipelines for environment pollution mitigation (Felli et al.).3) (v) The contribution of LARES to global climate change studies (Sindoni et al.).4) (vi) Smart disaster mitigation in Italy (Felli et al).5) (vii) Smart disaster mitigation in Thailand (Aimmanee et al.).6) In addition, Kubo, Tanaka, Maruyama and Asanuma started to develop a multi-layered deployable structural material system to dissipate wave energy by separating water flow and letting them collide. Challenges have been also done in industries and some are commercialized. Especially, neo RiSe flap-gate type seawall (Hitachi Zosen), SHELCAR (STARLITE Co., Ltd.), MOSE Project and Aqua Dam are attractive. Takenaka Corporation proposed innovative “Breakwater and breakwater group.” Toward future, Disaster Mitigation and Sustainable Engineering has to be brushed up to smartly overcome or rather utilize disasters.
Figure 1:
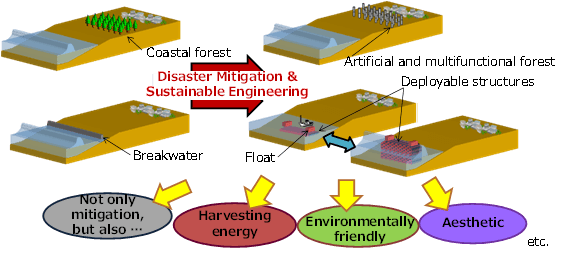
Typical examples to show the concept of “Disaster Mitigation and Sustainable Engineering.”
Recent Publications
- Asanuma H, et al. (2016) Disaster mitigation based on smart structures/materials. SPIE Vol. 9803, Paper No. 980302-1: 1-12.
- Shahinpoor M, Asanuma H (2015) Dynamic deployment of smart inflatable tsunami airbags (TABS) for tsunami disaster mitigation. Proc. ASME SMASIS2015, Paper No. 2015-8904: 1-4.
- Felli F, et al. (2015) Structural health monitoring of pipelines for environment pollution mitigation. Proc. ASME SMASIS2015, Paper No. 2015-8922: 1-7.
- Sindoni G, et al. (2015) The contribution of LARES to global climate change studies with geodetic satellites. Proc. ASME SMASIS2015, Paper No. 2015-8924: 1-7.
5. Felli F, et al. (2014) Smart disaster mitigation in Italy, Proc. ASME SMASIS2014, Paper No. 2014-7631, 1-8.
