Sundara Vadhana Gurushev
Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Dubai
Title: BioSkin Facades: A reinterpretation of the Mashrabiya
Biography
Biography: Sundara Vadhana Gurushev
Abstract
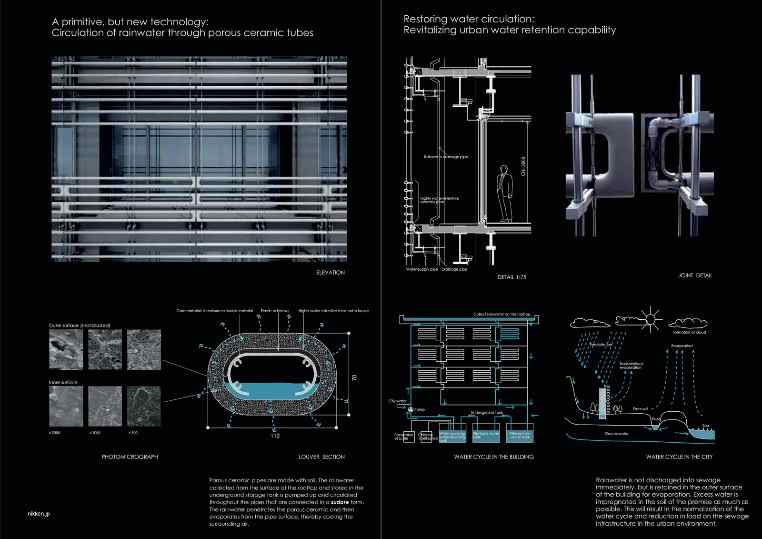
Archetype, in Jungian theory, is a primitive mental image inherited from the earliest human ancestors and supposed to be present in the collective unconscious. Identity refers to one’s unique façade, so to speak, in this case, a country’s history or culture. Vernacular Architecture is referred to as ‘Architecture of the People’. It becomes a language of form and culture which gives rise to identities unique to its context. Architectural identities, however, do not necessarily mean monuments or magnificent structures. The architectural identity of a region can be found in the most basic houses of the region. This study focuses on the vernacular design elements that can be reinterpreted and adapted into present day architecture of the gulf. Sudare, the famous Japanese bamboo blinds and Uchimizu, a Japanese air-cooling technique that uses water-spray to cool the surroundings. These were the foundations of the BioSkin Facade system, developed by Nikken Sekkei for the Sony Tower in Osaka back in 2011. The reinterpretation of two ancient techniques by infusing them with existing technology, won the company the CTBUH 2014 award for Innovation. The system uses ceramic pipes which have rainwater harvested on the rooftop running through them. These pipes are exposed to the heat of the buildings surroundings which lets the water evaporate, thus, cooling the immediate surroundings. This second skin facade of Sony Tower reduces its cooling load while also eliminating Urban Heat Island Effect. The concept is similar to that of a Mashrabiya found in the gulf region. The Mashrabiya in olden times was an intricately carved screen that sometimes had a pot of water that cooled the hot air passing through the screen. Applying a similar concept to the gulf region, the BioSkin Facades could be applied in this region as well. Although the system uses rainwater, something that is not found in the gulf; the water could instead be replaced with grey water, which is found globally and can be sourced from the building itself. This would mean the existence of a second skin system that can be adapted and used globally, even in regions where rainwater harvesting is not feasible.
Image
References
1. Oliver, P. (2014). Built to Meet Needs.
2. Yamanashi, T. &. (2011). BIO SKIN urban cooling facade. Architectural Design.
3. Fathy, H. (1989). Natural Energy and Vernacular Architecture: Principles and Examples with Reference to Hot Arid Climates. United Nations University.